The "pearl necklace" of the spine requires careful attention, if there is no proper prevention of diseases of the spine, symptoms of osteochondrosis appear. The treatment in this case is long, it is impossible to completely restore the integrity of the spine and cartilaginous discs.
In general, osteochondrosis is considered a change in bone tissue, ligaments, cartilage and intervertebral discs of the spine. This process is long, the changes do not appear "suddenly", but are felt at the first signs and characteristic symptoms. Most often it is mainly pain that occurs when nerve fibers, soft tissues or blood vessels are damaged. The signs of osteochondrosis directly depend on the stage of the disease and the area of the lesion, the treatment at each stage is different.
Clinical picture
Walking upright is a distinctive feature of a person like Homo sapiens and at the same time the vertical position is the main reason for the development of osteochondrosis. No member of the 4-legged fauna is aware of the symptoms of osteochondrosis. When walking upright, the intervertebral cartilage experiences a colossal load and over time they undergo changes, deformation occurs, the spine ceases to perform its functions completely.
Four groups of characteristic changes:
Neurological syndrome
Symptoms of nerve damage may include loss of skin sensitivity or decreased muscle strength. In osteochondrosis of the spine, the first sign of neurological disorders can be considered the appearance of pain, which is a consequence of compression or irritation of the spinal roots. The first signs are localized in a limited area of the back, where pathological changes have begun. As the pain progresses, it gradually "spreads" to all parts of the body located in the area of innervation of the compressed nerve root. First, the pain can be given to the arms or legs, this condition usually forms a misconceptionnot conducted properly.
In neurological syndrome, the symptoms of impaired motor function develop less frequently than sensitive ones. If this happens, then symptoms of partial or complete loss of mobility of the arm or leg may be observed, for example: in sacro-lumbar osteochondrosis of the spine, paresis of the left or right lower limb occurs.

Static syndrome
The first symptom appears when changes in the vertebrae begin. As a result, improper posture develops: lordosis, kyphosis or scoliosis. In difficult cases there is a restriction of the mobility of the articular surfaces of the spine, the signs of this are the inability to fully straighten or turn the head.
Vascular syndrome
Spinal vascular problems develop for the following reasons:
- Low tone of the sympathetic NA (signs of chronic ischemia of the internal organs).
- When local compression of blood vessels by altered vertebrae or their processes. The signs of osteochondrosis in this case are expressed in the violation of the blood supply to the brain when compressing large vessels. Symptoms of oxygen deficiency include dizziness, poor blood supply to the inner ear, or nausea. Symptomatic treatment, as a rule, does not give serious results.
Trophic syndrome
Such symptoms of osteochondrosis are characterized by the appearance of ulcers on the skin, which is a consequence of tissue malnutrition. Skin lesions occur in combination with neurological and vascular factors. The exact signs depend on which part of the back has been affected.
Typical manifestations of the pathology
Each part of the spine has its own typical signs of osteochondrosis, according to which a vertebral neurologist diagnoses the disease in both men and women. From these symptoms you can find out which parts of the back are affected and what treatment is needed first.
There are several types of osteochondrosis: thoracic, cervical, lumbar, sacral and mixed, when the localization of the signs is not in one department, but has a diffuse nature. The first signs of osteochondrosis in women and men begin to be felt with mild dull pain, discomfort, crunch, often with thoracic osteochondrosis, pain appears in the heart. Ideally, treatment should begin at this stage, then it will be possible to avoid all back problems in the future.
In addition, the signs of osteochondrosis become clear, painful sensations begin to be given to the hands or feet. The pain in the spine increases with each load and gradually it becomes problematic to perform movements that are associated with bending forward. The more osteochondrosis occurs, the more limited the mobility of the back, the thinned intervertebral discs lose their flexibility, the distance between the vertebrae decreases and their mobility is lost. The muscles begin to work in "emergency mode", being constantly tense, supporting the vertebrae to prevent them from coming together and completely destroying the intervertebral discs.
Tense muscles cause discomfort to a person even more, tension increases, soreness, symptoms of osteochondrosis increase.
Pathology of the cervix
Signs of cervical osteochondrosis often "hide" under the guise of other diseases. The first sign of neck pathology is a headache that cannot be relieved with conventional painkillers. It starts from the back of the head, going to the temples. Unpleasant sensations intensify after a long stay in one position, often tingling in the arm, shoulder blade and shoulder. With severe pinching of the nerve fibers, paresis or paralysis of the arm may develop.
When blood vessels are damaged, signs of a cerebrovascular accident appear:
- Tinnitus, dizziness - talk about poor blood flow in the cochlea and semicircular tubules.
- Reduced vision, flies in front of the eyes - indicate poor nutrition of the optical apparatus.
- Severe oxygen starvation of the brain - can manifest itself in sudden loss of consciousness, especially if cervical osteochondrosis is accompanied by atherosclerosis of the vessels.

Hiccups, shortness of breath, shortness of breath and panic attacks "speak" of damage to the phrenic nerve. The diaphragmatic nerve is part of the cervical plexus and is directly related to the regulation of the frequency and depth of breathing.
Breast pathology
The symptoms of thoracic osteochondrosis are quite varied, although this part of the spine is less commonly affected in both women and men. The painful sensations have a clear localization: the upper abdomen, the shoulder blades and between the ribs. But often osteochondrosis "hides" behind signs of intestinal or renal colic, angina pectoris or cholecystitis.
Symptoms showing a lesion of one or another breast segment:
- Upper thoracic segment. Feeling of a lump in the throat, violation of the act of swallowing, cough.
- Middle thoracic segment. Symptoms that mimic gastritis and ulcers (gastralgia) and symptoms with arrhythmia and hypertension (cardialgia).
- Lower chest segment. Symptoms of intestinal motility disorders and signs similar to those of appendicitis appear.
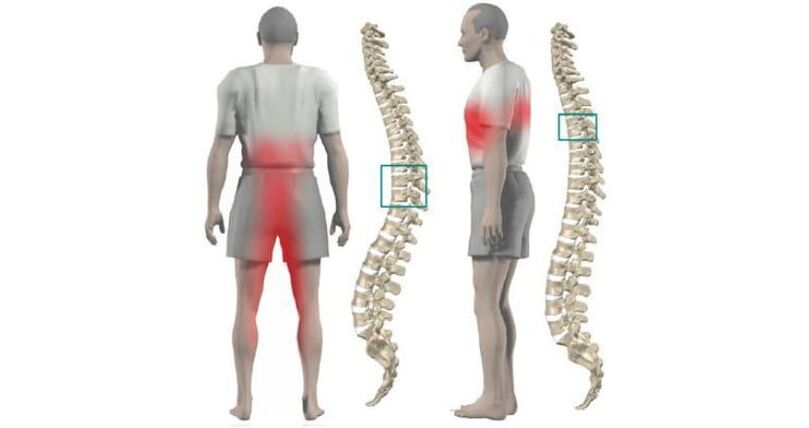
Lumbar pathology
Signs of damage to this area are extensive, but most often the first signs are felt with pain in the lower back and legs, loss of sensitivity and numbness of the skin of the lower extremities.
Changes in the lumbosacral region, characteristic symptoms:
- Pain and lumbago are observed after exercise.
- When the motor nerve fibers are pinched, paresis and paralysis of the legs develop.
- Pinching of nerves and blood vessels in men and women leads to pelvic disorders.
It should always be remembered that osteochondrosis of the spine is a hidden and insidious disease. You can treat the respiratory, genitourinary or gastrointestinal tract for years, but do not get positive results from therapy. Therefore, in case of signs of disease, it makes sense to consult primarily a neurologist and not a cardiologist, therapist or gastroenterologist.





































